A processing framework to access large quantities of whispered speech found in ASMR
Pablo Pérez Zarazaga, Gustav Eje Henter, Zofia Malisz
Citation information
@inproceedings{perez2023cwad,
title={A processing framework to access large quantities of whispered speech found in ASMR},
author={Pablo Pérez Zarazaga and Gustav Eje Henter and Zofia Malisz},
booktitle={Proc. ICASSP},
year={2023}
}
Summary
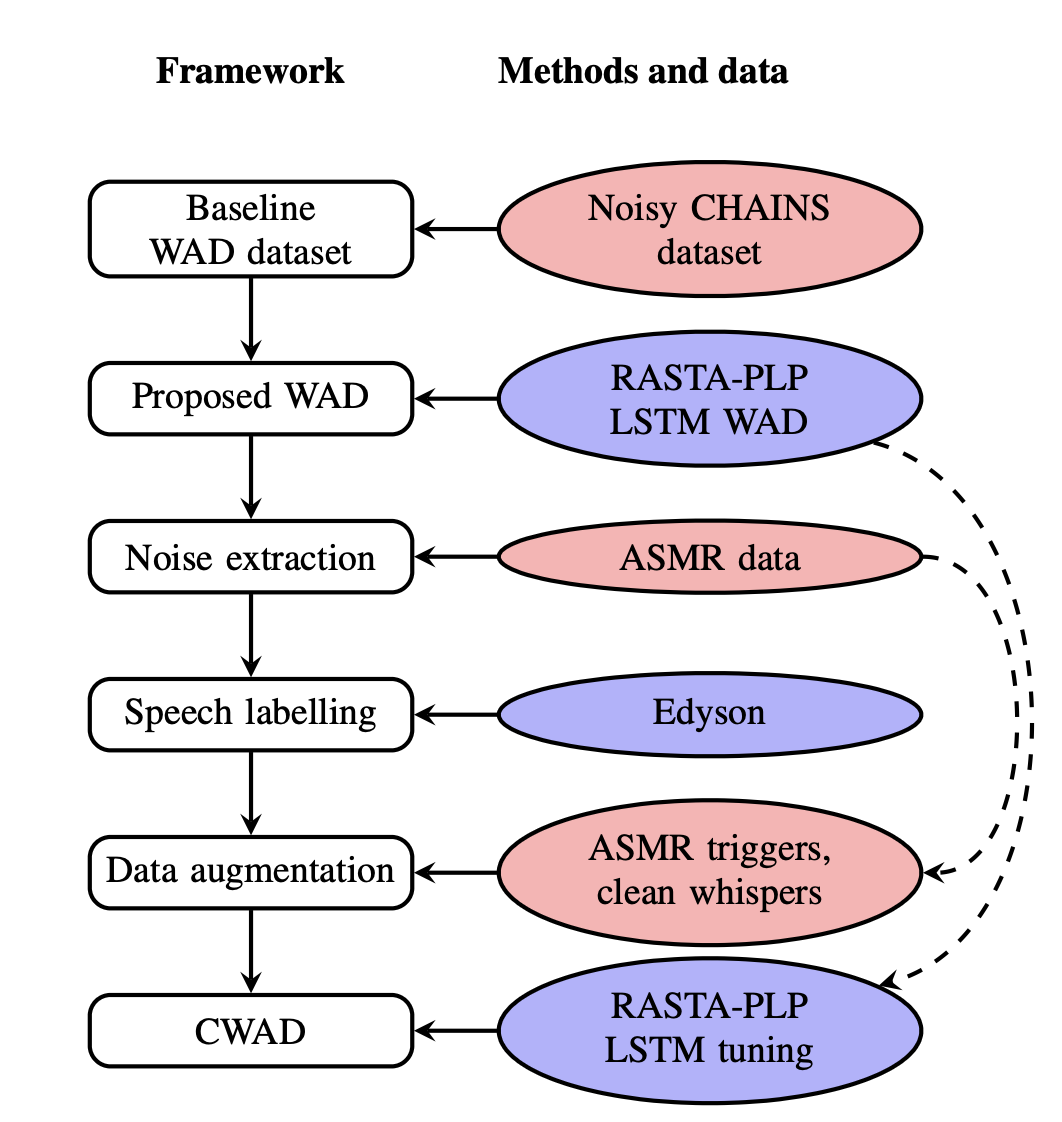
The goal of this work is to develop a framework for whisper activity detection (WAD) for extraction of clean whisper unaffected by noises for whispered data collection.
One of the main problems in the analysis of whispered speech is the limited amount of data available, and most specifically, spontaneous whispered speech. A great source of whispered speech data are ASMR recordings available in streaming platforms like YouTube or Twitch. For that reason we propose to use tools like Youtube-DL to collect ASMR recordings, which can be used as a source of whispered speech.
We propose to train a WAD method on a synthetic noisy whispered dataset. The trained model is then used to detect whispered speech in ASMR recordings. Using Edyson to more accurately separate segments into “clean whisper” - “noisy whisper” - “noise”.
The separated ASMR data is used for speech data augmentation and the proposed clean WAD (CWAD) model is trained using the specific ASMR triggers as noise.
ASMR data is used as an example of a great source of whispered speech available online. However, this framework could be adapted to other noisy whispered speech sources.
For more information, please see our paper at ICASSP 2023.
Visual overview
Code
Code will be made available in our GitHub repository shortly.
Whisper activity detection
The following audio samples show the classification of ASMR segments by the CWAD method into clean whispered speech and speech affected by ASMR triggers or noise.
In the first set of recordings we observe relatively clean whispered speech with distinct noises like microphone rubbing or tapping. Whispered speech is clearly detected, and removed when it is combined with these type of distinctive noises. Breathing sounds, however, are more challenging as they are produced isolated from speech and also at the beginning of some words, therefore, the inintial moments of some words are still considered as noise.
| Speaker | Original ASMR sample | CWAD Clean Whispered Segments | CWAD Noisy Whispered Segments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | |||
| Female |
In the second set of samples, we can see a different type of whispered speech used in ASMR, known as “inaudible whisper”. This type of speech contains more breathing sounds and sometimes it is hard to distinguish the actual speech. However, it can still be detected as whispered speech when it is found in relatively clean environments.
| Speaker | Original ASMR sample | CWAD Clean Whispered Segments | CWAD Noisy Whispered Segments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | |||
| Female |
Finally, we can observe a set of different mouth sounds produced by the “ASMRtists” and more stationary noises due to the background in the recordings and continuous triggers like microphone rubbing. The system separates the segments with clean speech from those combined with noises like microphone rubbing and other mouth effects, but the constant background noise reduces the accuracy of the detection. It is still to be determined if a certain level of background noise would be acceptable in these recordings or it should be removed before the analysis.
| Speaker | Original ASMR sample | CWAD Clean Whispered Segments | CWAD Noisy Whispered Segments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | |||
| Female |